
click and email your enquiry to us
Back to the last page


|
Contact Us │ | Index | |
click and email your enquiry to us Back to the last page |
  |
||
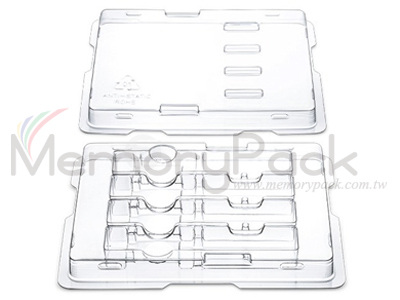
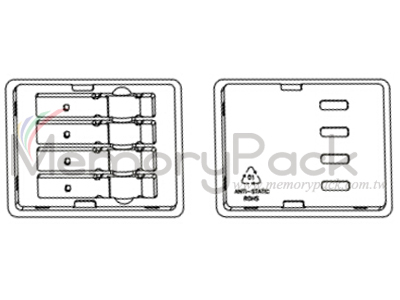
| Model 4ctQSFP28 ( tray for 4-count QSFP+ / QSFP28 / XFP / QSFP transceivers ) | ||
 |
 |
 |
| Model | 4ctQSFP28 ( tray for 4-count QSFP+ / QSFP28 / QSFP / XFP transceivers ) | |
| Specification | Tray for 4-count QSFP+ / QSFP28 / XFP | |
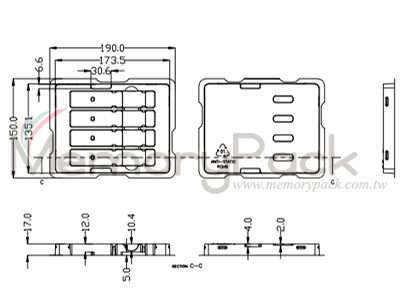
| Dimension | 190mm(Length) x 150mm(Width) x 17mm(Height) | |
| Details about the carton | Model 4ctQSFP28 = ? pieces = 1 carton = ? x ? x ? mm = ? cubic feet = ? KGS (?) CTN NO.? | |
| Others Tray (190mm x 150mm Tray Series) | |
 |
 |
| QSFP28 vs QSFP+ ( Difference Between QSFP28, QSFP+ ) |
Usually QSFP28 modules can't break out into 10G links. But it's another case to insert a QSFP28 module into a QSFP+ port if switches support. At this situation, a QSFP28 can break out into 4x10G like a QSFP+ transceiver module. One thing to note is that you can't put a QSFP+ transceiver into a QSFP28 port to avoid destroying your optics. |
| QSFP+ MTP/MPO vs QSFP+ LC ( Difference Between 40G QSFP+ Transceiver With LC Interface And MTP/MPO Interface ) |
|
If you need more information, please contact with us
E-mails:
rfqmpk@gmail.com;barret-chen@memorypack.com.tw;superpolu@gmail.com;shop@memorypack.com.tw;sales01@memorypack.com.tw;sales03@memorypack.com.tw;sales05@memorypack.com.tw;sales08@memorypack.com.tw;shinly@ms18.hinet.net
E-mails:
rfqmpk@gmail.com
barret-chen@memorypack.com.tw
superpolu@gmail.com
shop@memorypack.com.tw
sales01@memorypack.com.tw
sales03@memorypack.com.tw
sales05@memorypack.com.tw
sales08@memorypack.com.tw
shinly@ms18.hinet.net
Websites:
www.memorypack.com.tw/px/px.html
www.memorypack.com.tw
www.shinly.com.tw
www.wjp-memorypack.com
www.cputray.com
www.sfptray.com
transceiver tray
transceiver clamshell
transceiver container
transceiver plastic box
transceiver packaging
optical transceiver tray
optical transceiver clamshell
optical transceiver container
optical transceiver plastic box
optical transceiver packaging
QSFP28 tray
QSFP28 clamshell
QSFP28 container
QSFP28 plastic box
QSFP28 packaging
QSFP+ tray
QSFP+ clamshell
QSFP+ container
QSFP+ plastic box
QSFP+ packaging
QSFP tray
QSFP clamshell
QSFP container
QSFP plastic box
QSFP packaging
XFP tray
XFP clamshell
XFP container
XFP plastic box
XFP packaging
光纖收發器塑膠盒
光電轉換器塑膠盒
QSFP28塑膠盒
QSFP28包材
QSFP28塑膠電子盤
QSFP28電子盤
QSFP28抗靜電盒
QSFP+塑膠盒
QSFP+包材
QSFP+塑膠電子盤
QSFP+電子盤
QSFP+抗靜電盒
光纖收發器塑膠盒
光纖收發器包材
光纖收發器塑膠電子盤
光纖收發器電子盤
光纖收發器抗靜電盒
光電轉換器塑膠盒
光電轉換器包材
光電轉換器塑膠電子盤
光電轉換器電子盤
光電轉換器抗靜電盒
Memorypack Industrial Co., Ltd
POLU industrial Ltd
Shinly Plastics corporation
WJP memorypack Industrial Co., Ltd
gbic-t transceiver clamshell plastic box blister case
Transceiver packaging plastic box clamshell gbic sfp sfp plus xfp xenpak x2
What are transceivers?
A transceiver in simple terms can be defined as a device that comprises of both a transmitter and a receiver of analog or digital signals.
Radios and telephones are some of the devices that use transceivers. Network transceivers are used in specific networks like LAN to transmit signals.
Lots of people tend to confuse transceivers and transponders ere is the difference; a transceiver transmits and receives signals anytime while a transponder
only responds to an incoming signal or command.
Transceivers come in three configurations; the chip, board and module style. The chip style is portable and the smallest optical transceiver available.
The board Style unlike the chip style, is in-built in the network system making it permanent while the module Styles are stand-alone devices as they
are not directly installed in the network system.
Modes of Channel operations
Fiber optic transceivers operate in three modes of channels; the simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex modes.
1. The Simplex mode: This mode of channel operation is one way. It does not send back error information. Since it is one way,
its use is phasing out and todayit is mainly used in radios.
2. Half-duplex mode: This can only handle a single signal at a time. That is; it can only transmit or receive a signal at a time. Not both.
3. Full-duplex mode: A full-duplex transceiver can handle the reception and transmission of all signals at once. One thing to note though
is that the transmitter and receiver need to work on different frequencies in order to avoid collisions between transmitted and reception signals.
Some of the types of Transceivers we offer
GBIC: GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter) is the media conversion device that connects Gigabit network equipment and fiber optic networks. By use of a GBIC transceiver,
Gigabit network equipment can connect to single mode ports, multimode fiber ports and even copper wires. GBIC is also hot pluggable which enables connection modifications.
SFP: SFP in full is Small Form- factor Pluggable. They are also referred to as mini GBIC due to their similarity in function to the GBIC transceivers though smaller in size.
SFP transceivers are mainly used to link equipment in telecom and data communications like switches and routers. They support applications like Fiber-to-the-desktop (FTTD),
SONET/SDH Network, Gigabit Ethernet, and High-speed computer links among others.
SFP Plus (SFP+): These are an upgraded version of the SFP. The only difference is that they can support up to 10Gbps data rates and are smaller than the 10Gbps X2 and
Xenpak transceivers.
XFP: These are protocol independent optical media conversion equipment used in the SONET/SDH Network, 10G Ethernet and Fiber channel applications. XFP transceivers
are currently the cheapest and the smallest transceivers.
XENPAK: These transceivers support all optical transceiver ports defined in the IEEE 802.3ae. Covering up to 10Km via a G652 multimode fiber he Xenpak transceivers
come in three types which include; Xenpak 10GB SR, Xenpak 10GB LR and the 40km Xenpak 10 GP ER.
X2: These function exactly like the Xenpak because they were built on the Xenpak standards. These optical transceivers?10G Ethernet standards were defined by IEEE in 2002.
MPK
Memorypack
Memorypack Industrial Co., Ltd
CPU pack industrial Co., Ltd
POLU industrial Ltd
WJP memorypack industrial Co., Ltd
Shinly Plastics corporation